Cellulite is enlarged “pockets” of fat cells that are pushed to the surface of the skin by inflexible connective tissues. It mainly affects women. Cellulite is seen as uneven skin consisting of dimpling, together with accompanying raised areas. It is most common on the buttocks and buttock area, but can also be seen on the arms and abdomen area. It is often referred to as orange skin syndrome. In cases where the patient has cellulitis, he has an increased number of fibrous septae (connective tissues) that tighten and harden, making the skin less flexible. This creates the “pockets” of fat cells, and subsequently the illusion of dimpling. Most women have this problem, but it is often more visible in overweight patients. Cellulitis is rarely seen in men. It is caused by 3 main biological factors – a thicker layer of hypodermal fat, a decrease in collagen, and hardening of fibrous septae.
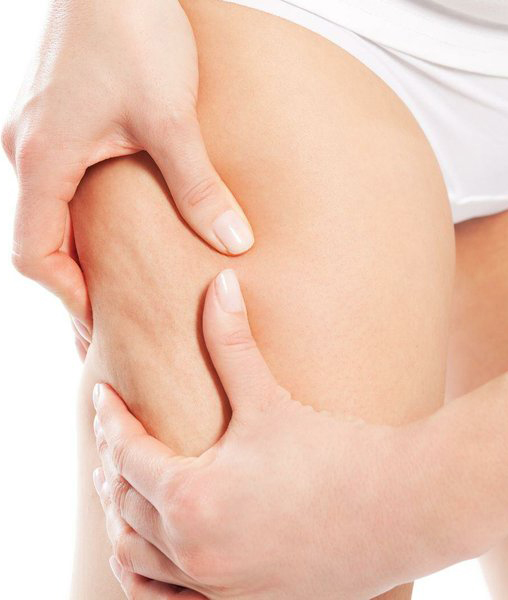
Cellulite is a specific skin condition. This type of imperfection is most commonly seen on the thighs and buttocks, but sometimes also on the arms and abdomen. It is a visible irregularity in the upper dermal layer (hypodermis), which has earned it the name 'orange skin'.When cellulite forms, the relief in the area is distorted due to unevenly accumulated subcutaneous fatty tissue. These form so-called 'pockets', which are pushed into the hypodermis over time by inflexible connective tissues. As a result, bumps are formed in the form of 'dimples' and often entire areas are significantly raised above the rest. As soon as it undergoes a really serious enlargement, the skin becomes uneven and dangerously squeezed by lymphatic and blood vessels. Thus, microcirculation is impeded and slowed down and cellulite becomes not only a cosmetic problem but also a health problem.
Cellulite mainly affects ladies. According to statistics, 90% of patients with this dermatological problem are female and only 10% – male. The three main biological factors causing cellulite are thickening of hypodermal fat, decreased secretion of collagen in the body and hardening of fibrous septae. Contemporary medical experts emphasize that these risks are increased when present:
Hormonal disturbances (mainly related to estrogen, adrenaline, prolactin, insulin and most thyroid hormone levels);
Genetic predisposition (ethnicity, inherited diseases related to blood circulation and some forms of metabolic disorders);
Unhealthy habits (improper diet with too much fat, fast carbohydrates and salt, lack of any physical activity, smoking, abuse of alcohol and certain medications, dehydration and stress);
Rapid weight gain, including in the presence of pregnancy.
How visible and difficult to remove is cellulite (stages / degrees of cellulite)
Regardless of the choice of a specific cellulite removal therapy, its effect and the first visible results depend mainly on the stage of the skin problem. Unfortunately, in most cases, ladies start seeking professional help and aesthetic services at a relatively advanced one. Also known as grade, the severity of cellulite is divided into the following levels according to the Nuremberg-Mueller scale:
0 (no visible signs) – with the naked eye, no traces of cellulite are observed, but very small insignificant dimples are noted when the skin is pressed;
1 (mild) – most of the time there are no visible signs of cellulitis, but when squeezed the dimples are significantly larger in size and peculiar in shape;
2 (moderate) – the ‘orange skin’ is visible in both standing and sitting (or other) positions. Usually at this stage cellulite is not yet noticeable in the supine position;
3 (severe) – the bumps are noticeable in any body posture.
In addition to the degree of manifestation, there are several distinct types of cellulite. The division of these categories is important not only for making a diagnosis – hence a correct assessment of whether it is purely cosmetic or medical (with health risks), but also for determining the most appropriate therapy. In theory and practice, the following types of cellulite are usually distinguished:

Mild or the most common type of cellulite is visible both at rest and under pressure, and can affect literally all parts of the body, but is most often concentrated on the buttocks and thighs. Almost always, water retention is seen throughout the body and bumps are felt when touched on the affected area. The skin is usually very loose, but the musculature is also undertoned. Although it sounds like the scariest type, this cellulite is treated most successfully and quickly;

Firm – also known as compact, it is the most difficult to remove. The reason has to do with its formation, suggested by its name, namely: tissue hardening. This cellulite is usually visible on the thighs and buttocks, and pain can even be felt in the affected area when touched. It is often caused not only by a sedentary lifestyle, but also by long untreated obesity;

Oedema cellulite is usually seen on the lower legs. It is often called medical because it is caused due to impaired microcirculation. There may also be lymphatic stasis, i.e. significant retention of excess fluid, which is not always accompanied by excess weight;

Athletic – as strange as it may sound, there is such cellulite and yes, it is typical for athletes. It is caused by excessive physical activity. It occurs as a result of overexertion of certain parts of the body at the expense of others. It is rarely seen on the classic cellulite sites such as the buttocks and thighs;

Fibrosis – it is similar to hard cellulite, the difference being that in fibrosis there is usually an inflammatory process in the tissues and it is also always caused by lack of physical activity.